general ideas
- distribute data across multiple databases through some heuristic that splits data evenly.
- sometimes based on user ids, last names, or geographical location.
- has similar advantages to database-federation because each individual database is smaller.
- high-level disadvantages.
- adds complexity in application code.
- data can become lopsided because of power users or inconsistent hashing.
- joining data is more complex.
- adds more hardware.
different ways to partition
range partitioning
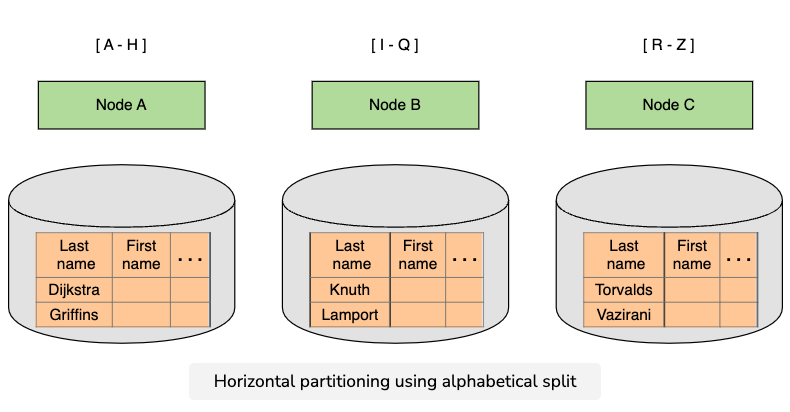
- split up the data based on the range of some field.
advantages
- easy implementation.
- range queries are fast when all the data is in a single node.
- ranges can be adjusted with only two nodes needing to be involved.
disadvantages
- can’t perform range queries with a key other than the one used to partition.
- can have uneven distribution in traffic based on which key was used to partition.
hash partitioning
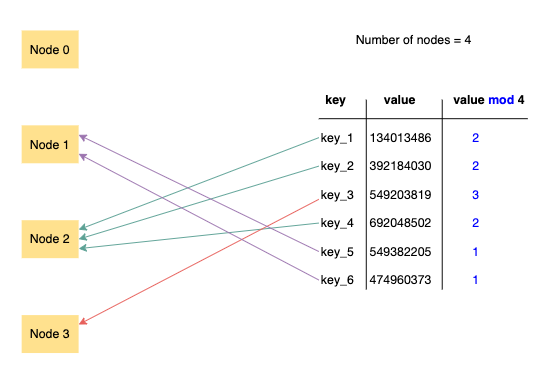
- apply a hash function to an attribute to determine which partition a piece of data goes into.
- we do this for every new record, and use the same hashing function to find out where to find an existing record.
- we hash the value in the attribute, then do modn where n is the number of nodes we have.
- this method can be improved with consistent hashing.
advantages
- partition mapping can be calculated at runtime.
- greater chance then range partitioning for the nodes to be distributed evenly.
disadvantages
- can’t perform range queries at all without storing additional data.
- adding or removing nodes causes repartitioning across all nodes in the system.
- consistent hashing.
- adding or removing nodes only affects neighboring nodes on the ring.
references

