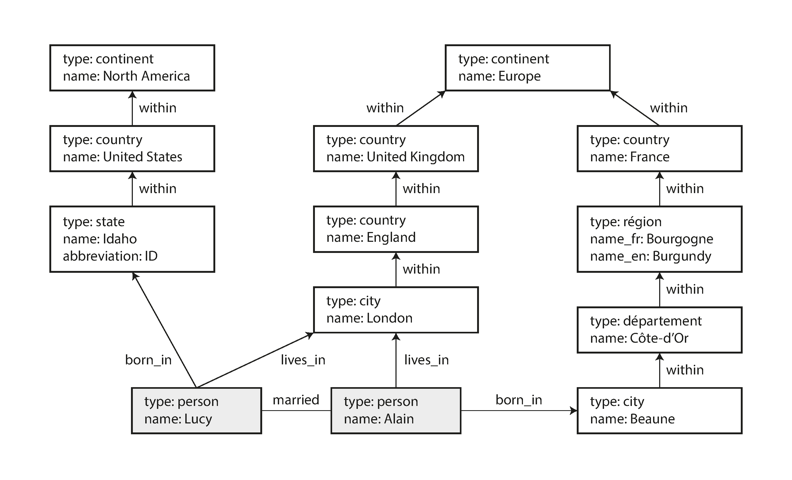
a database in which each node is a record and each edge is a relationship between nodes.
pros
- useful for modeling complex relationships like social networks.
- great for evolvability; they can be easily extended to include new entities or relationships.
how are graph databases structured?
the actual data-modeling of graph databases is implemented in several different ways.
property graph
this format is used by neo4j, titan, and infinitegraph.
class PropertyGraphNode:
self.id = "unique_id"
self.outgoing_edges = set()
self.incoming_edges = set()
self.properties = {}
class PropertyGraphEdge:
self.id = "unique_id"
self.tail_vertex: PropertyGraphNode = None
self.head_vertex: PropertyGraphNode = None
self.label: string = "in"
self.properties = {}triple-store
this format stores all datapoints as tuples of length 3, in the form (vertex_a, vertex_b, relationship).
