News Feed System
- clarifications.
- supports both mobile and web.
- users can publish posts and see their friends’ posts.
- sorted by reverse chronological order.
- users can have 5000 friends.
- ten million daily active users.
- posts can have images and videos.
- high level design.
- feed publishing.
- we will have an endpoint for a user to send a request with content to create a newsfeed post.
- this will be sent to three services.
- saved in post database and cached.
- sent to a newsfeed cache for their friends to see.
- a notification service to notify friends that a new post has been created.
- newsfeed building.
- everytime a user asks to retrieve their feed, we check the newsfeed cache and return it.
- feed publishing.
- deep dive.
- web servers should have authentication and rate-limiting.
- fanout service.
- we can either fanout on read or write (push vs. pull).
- on write.
- we precompute the newsfeed when a new post is written.
- if a user has many friends, write process can take a while as many newsfeeds have to be updated.
- inactive users do not need to have their newsfeeds updated so often.
- on read.
- the above problems are solved, but fetching newsfeeds can be slower.
- we can use a hybrid model, which is to use a on-write model for most users, but use an on-read model for the follower’s of celebrities.
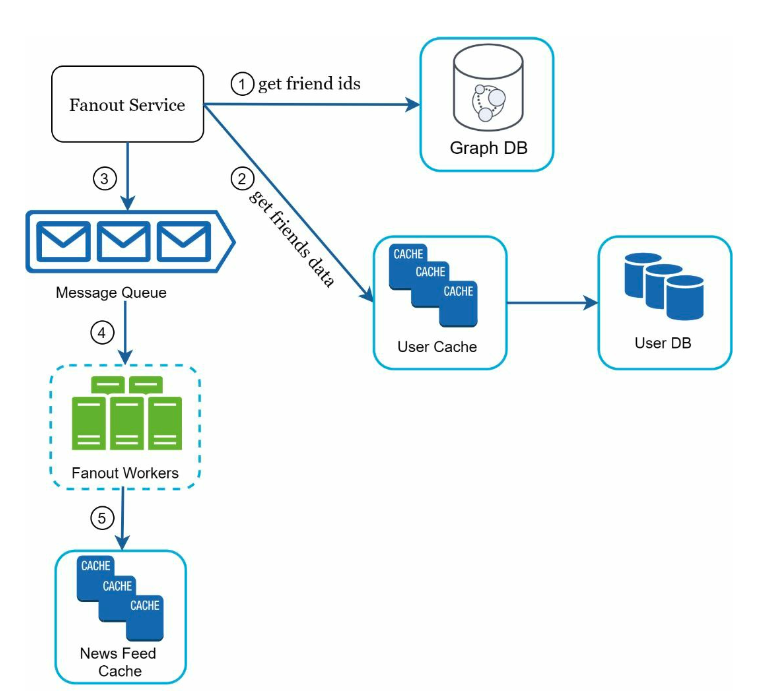
- store friend relationships in a graph database.
- friend info is saved in a database and cached as well.
- the newsfeed cache only has to store user ids and post ids pairs, to keep storage size lower.
- store this per user.
- this is done asynchronously with a message queue.
- when a user requests their feed, we take these ids and fetch these posts and users from our caches and databases.
- there’s an opportunity to discuss how many and what caches we need, such as storing popular content in a separate cache, and storing two caches for followers and following (assuming our caches are stored in a hashmap type orientations).
- further discussion.
- vertical scaling vs. horizontal scaling.
- scaling the database.
- stateless web architecture.
- monitoring.
Categories:: system-design