Given the root of a binary tree, the value of a target node target, and an integer k, return an array of the values of all nodes that have a distance k from the target node.
You can return the answer in any order.
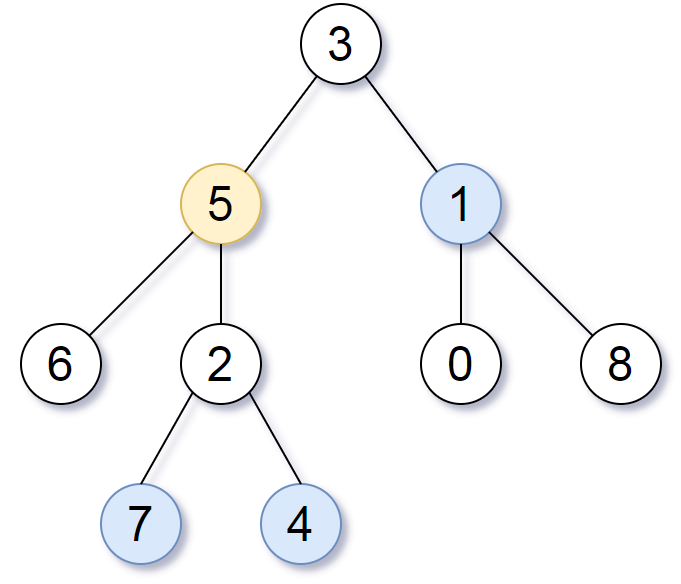
solution
We do a traversal to get parent pointers for every node. Then, we can simply traverse the tree like a normal graph from the target node.
def distanceK(self, root: TreeNode, target: TreeNode, k: int) -> List[int]:
# generate parent pointers
parents = {}
def dfs(node, parent):
parents[node.val] = parent
if node.left:
dfs(node.left, node)
if node.right:
dfs(node.right, node)
dfs(root, None)
# BFS from target node
res = []
q = deque([(target, 0)])
visited = set([target.val])
while q:
cur, depth = q.popleft()
if depth == k:
res.append(cur.val)
if depth > k:
break
for neighbor in [parents[cur.val], cur.left, cur.right]:
if neighbor and neighbor.val not in visited:
visited.add(neighbor.val)
q.append((neighbor, depth+1))
return res