There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1.
solutions
bfs with priority queue
We do a bfs with a priority queue to always advance our bfs to the cheapest next node first. This guarantees that the first time we reach the destination, that is the cheapest path to reach it.
We know that the first time we reach dst, it must be the optimal solution, because our BFS using a priority queue performs a “best-first-search”.
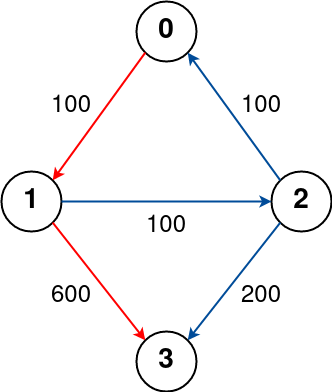
We don’t actually need to store the best score we’ve seen for a node, because we’ll always visit the best score for a node first. So, the only thing we need to store, as a special constraint for this problem, is the fewest stops it has taken us to reach a certain node. Consider the example below. We’ll traverse src->1->2->3 before taking the src->3 route, but we’re OK to update visited[3] because the optimal dst path has already been added to the queue.
If there was a longer path from 3->dst that contained negative weights, updating visited[3] would allow us to explore it if k was a constraint, because the src->1->2->3 path might miss it due to already using too many stops.
def findCheapestPrice(self, n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int) -> int:
g = collections.defaultdict(list)
for fr, to, prc in flights:
g[fr].append((to, prc))
# heap[i] = (weightsofar, stopssofar, node)
# we start with the src, and no cost
minHeap = [(0, -1, src)]
# stop: min num_stops seen for node
visited = {}
while minHeap:
w1, s1, n1 = heapq.heappop(minHeap)
visited[n1] = s1
if n1 == dst and s1 <= k:
return w1
elif s1 > k:
continue
for neighbor, weight in g[n1]:
if neighbor not in visited or visited[neighbor][1] > s1+1:
heapq.heappush(minHeap, (w1+weight, s1+1, neighbor))
return -1level-order BFS with best-costs
Instead of using a priority queue, we can just level-order BFS, keeping track of the best cost we have to reach a node at any level.
We are only allowed to BFS to k+1 levels (k stops). During these levels, we only revisit a node if we reach a node and the new cost to reach it is less than the currently calculated one. (Kind of similar to Djikstra’s algorithm).
def findCheapestPrice(self, n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int) -> int:
g = defaultdict(list)
for u, v, cost in flights:
g[u].append((v, cost))
# dists[node] = best score
dists = [inf]*n
dists[src] = 0
q = [(0, src)]
stops = -1
while q and stops < k:
next_frontier = []
current_frontier_length = len(q)
for _ in range(current_frontier_length):
cur_cost, cur = q.pop()
for neighbor, cost in g[cur]:
total_cost = cur_cost + cost
if total_cost < dists[neighbor]:
dists[neighbor] = total_cost
next_frontier.append((total_cost, neighbor))
stops += 1
q = next_frontier
return -1 if dists[dst] == inf else dists[dst]