Given two strings word1 and word2, return the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
solutions
recursion with memoization
We maintain two pointers, one on each string. At any point in time, there are two scenarios:
- The two characters we are looking at match, and so no edit is required. We move onto the next pair of characters.
- The two characters don’t match. We can either replace one character to match the other, delete one of them, or insert one to match the other.
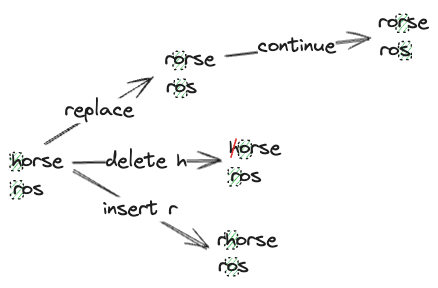
See the diagram for a visualization:
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
# always make s1 the longer string
if len(word2) > len(word1):
word1, word2 = word2, word1
memo = {}
def recurse(p1, p2):
"""
we've reached the end of one/both of the words
any remaining characters in the other word
can be inserted/deleted
"""
# base case
if p1 == len(word1) or p2 == len(word2):
if p1 == len(word1):
return len(word2) - p2
else:
return len(word1) - p1
if (p1, p2) in memo:
return memo[(p1, p2)]
# if chars are the same, no edit necessary
if word1[p1] == word2[p2]:
memo[(p1, p2)] = recurse(p1+1, p2+1)
return memo[(p1, p2)]
memo[(p1, p2)] = min(
recurse(p1+1, p2+1), # replace
recurse(p1+1, p2), # delete
recurse(p1, p2+1) # insert
)+1
return memo[(p1, p2)]
return recurse(0, 0)2d dynamic programming
We essentially reproduce the solution above, but use a 2d array instead of recursion with a cache.
Note that we go top-down (reverse iterate through the array), to mimic the behavior that the recursive method uses. This is useful when trying to directly convert solutions from recursion to DP (instead of having to reason about a bottom-up approach).
def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
dp = [[1000] * (len(word2) + 1) for i in range(len(word1) + 1)]
# base cases for when we reach the end of
# the shorter string
for j in range(len(word2) + 1):
dp[len(word1)][j] = len(word2) - j
for i in range(len(word1) + 1):
dp[i][len(word2)] = len(word1) - i
for i in range(len(word1) - 1, -1, -1):
for j in range(len(word2) - 1, -1, -1):
if word1[i] == word2[j]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j + 1]
else:
dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j + 1])
return dp[0][0]