Given an integer array nums, return the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence.
solutions
obvious dynamic programming solution
- create an array
dpof lengthnumsto store the longest subsequence ending at at . - at each index, we iterate through the entirety of
dp, and if we see a number that’s less than the current number at index , we setdp[i]todp[j]+1. - this takes .
# O(n^2)
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [1] * len(nums)
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
for j in range(i):
if nums[i] > nums[j]:
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1)
return max(dp)creating optimal subsequence in order
- we try to create the optimal subsequence by keeping track of a increasing subsequence in
sub.- if the next number we see is greater than the entire sequence, we append it to the end of the sequence.
- else, we replace the first number bigger than the current number in the subsequence with the current number.
- this is because we’re trying to optimize the subsequence to be as “small” as possible.
- in the end, the optimal subsequence is in
sub.
# input
nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
# example sub
[10]
[9]
[2]
[2, 5]
[2, 3]
[2, 3, 7]
[2, 3, 7, 101]
[2, 3, 7, 18]# O(nlogn)
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
sub = []
for num in nums:
i = bisect_left(sub, num)
# If num is greater than any element in sub
if i == len(sub):
sub.append(num)
# Otherwise, replace the first element in
# sub greater than or equal to num
else:
sub[i] = num
return len(sub)segment tree dp
Instead of using to search back in the DP array, we can use a segment-tree to update/search for the best increasing subsequence ending with a value in some range.
After doing compression on the array, we can construct the segment tree, and then iterate through each value. At each value, we find the best increasing subsequence so far that ends with some value in the range , where is the current value in the array.
We can find this in logarithmic time, as each TreeNode stores the length of the longest increasing subsequence for a given range.
We update our global answer, and then update the specific best for the given value in our segment tree. Notice that we have to update every level of nodes that contain in its range recursively.
This is what the empty segment tree looks like for a length 6 array.
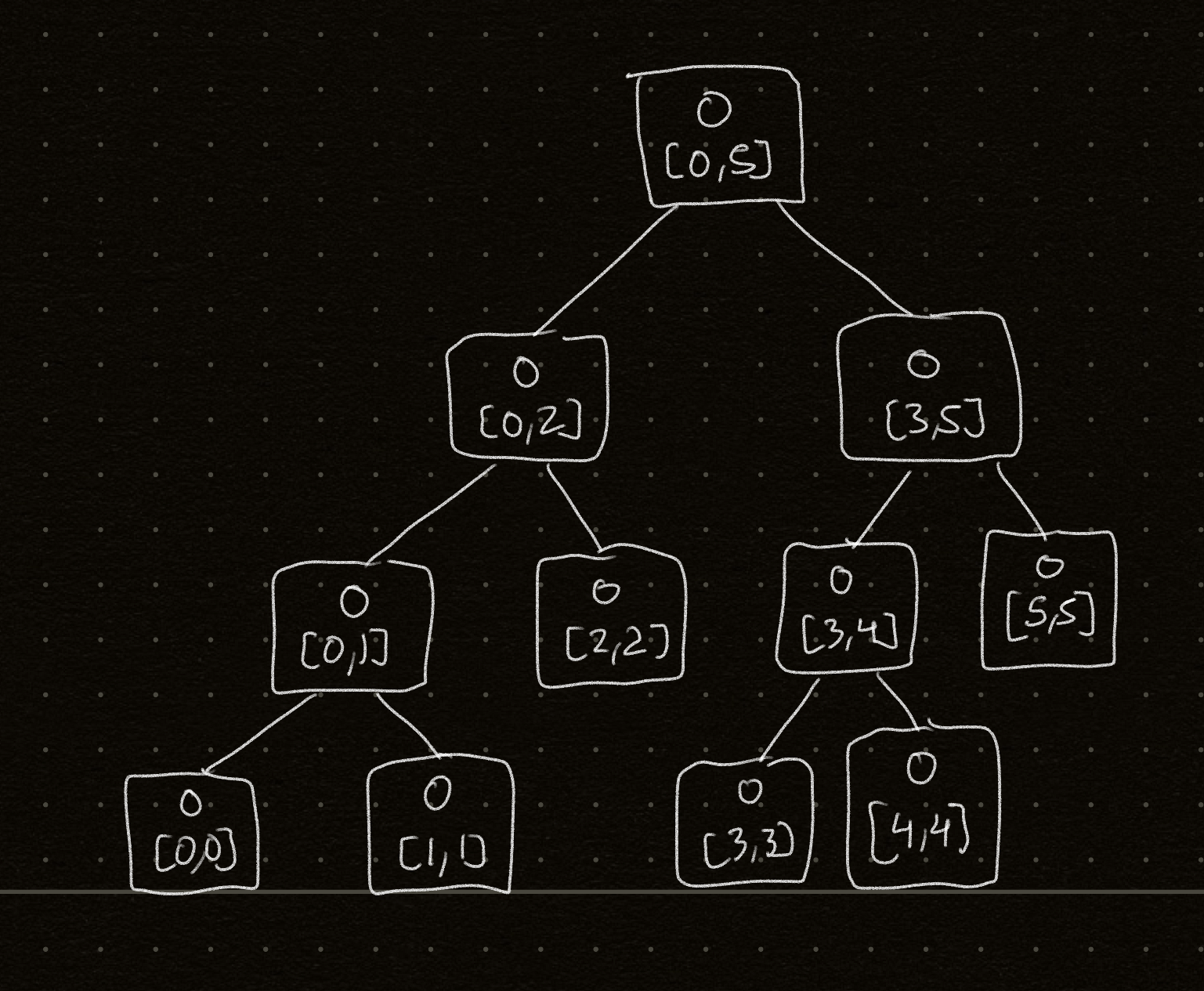
# val at TreeNode is the longest sequence ending at node.val
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, lo, hi):
self.lo = lo
self.hi = hi
self.val = 0
self.left = None
self.right = None
def __repr__(self, level=0):
indent = " " * level
result = f"{indent}TreeNode(lo={self.lo}, hi={self.hi}, val={self.val})\n"
if self.left:
result += self.left.__repr__(level + 1)
else:
result += f"{indent} None\n"
if self.right:
result += self.right.__repr__(level + 1)
else:
result += f"{indent} None\n"
return result
class SegmentTree:
def __init__(self, nums):
self.nums = nums
self.root = self.build(0, len(self.nums)-1)
def build(self, l, r):
if l == r:
return TreeNode(l, r)
m = (l+r)//2
left_tree = self.build(l, m)
right_tree = self.build(m+1, r)
node = TreeNode(l, r)
node.left = left_tree
node.right = right_tree
return node
def query(self, root, l, r):
if r < root.lo or l > root.hi:
return 0
if l <= root.lo and r >= root.hi:
return root.val
return max(
self.query(root.left, l, r),
self.query(root.right, l, r)
)
def update(self, root, index, value):
# disjoint, no update
if root.lo > index or root.hi < index:
return root.val
# leaf node
if root.lo == root.hi and root.lo == index:
root.val = value
return root.val
# node contains range for index we wanna update
# continue search to update correct node
root.val = max(
self.update(root.left, index, value),
self.update(root.right, index, value)
)
return root.val
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(nums)
# turn numbers into compressed range
# smallest number -> 0
# biggest number -> n-1
def compress(nums):
res = []
sorted_nums = sorted(nums)
for num in nums:
res.append(bisect_left(sorted_nums, num))
return res
nums = compress(nums)
tree = SegmentTree(nums)
res = 1
for num in nums:
local_max = tree.query(tree.root, 0, num-1) + 1
res = max(res, local_max)
tree.update(tree.root, num, local_max)
return res