You are given a 0-indexed array nums comprising of n non-negative integers.
In one operation, you must:
- Choose an integer
isuch that1 <= i < nandnums[i] > 0. - Decrease
nums[i]by 1. - Increase
nums[i - 1]by 1.
Return the minimum possible value of the maximum integer of nums after performing any number of operations.
solutions
First of all, it’s important to reframe this question as a a sort of “transferring of value” from the right towards the left.
Notice that when we decrease nums[i] by 1, we “give” it to nums[i-1]. Transitively, this single unit can then continue travelling leftward as far as the beginning of the array. Logically, this means that any value at can transfer value to any other index .
Conversely, this means that we can never transfer any units rightwards.
In this view, our end goal is to “distribute” the wealth as evenly as possible, with the constraint that we can only transfer things leftwards.
iterative scan with prefix sum array
From the above intuition, we can derive some insights from base cases:
- The optimally distributed maximum height in an array of length 1 will be equal to the height of the single bar.
- For two bars, if the bar at is taller than the bar at , then the best maximum height is the ceiling of the average of the two bars.
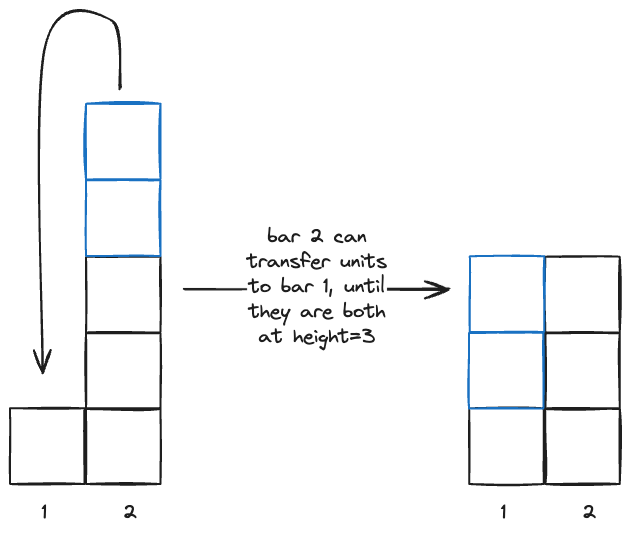
- However, if the left bar is taller, then the optimal maximum is simply the height of the left bar, because we can’t transfer anything rightwards.
- This leads to the intuition that as we scan rightwards through the bars and keep track of an optimal height, we can never improve on it, because even if we see a shorter bar later on, this bar can’t take the load off of any prior bars.
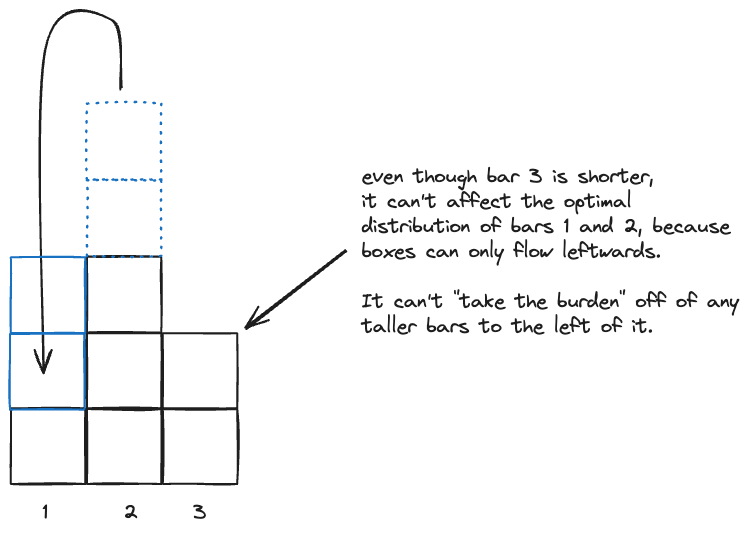
- Given any number of monotonically increasing bars, the optimal distribution will lead to a maximum bar height of
math.ceil(average(sum(bars))).
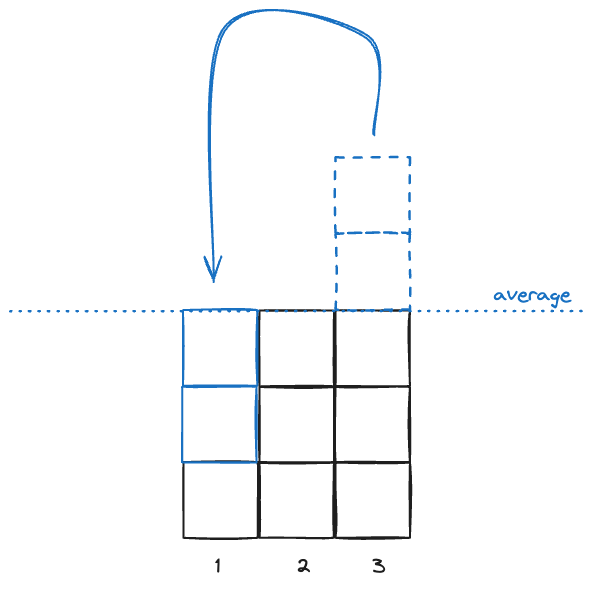
Given this intuition, we realize that we can scan through the array from left to right, computing the average of all the bars from to , and comparing that to our previous best.
Our running best can only get worse, hence the line ans = max(ans, math.ceil(average)).
def minimizeArrayValue(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
prefix_sum = [nums[0]]
ans = nums[0]
for num in nums[1:]:
prefix_sum.append(prefix_sum[-1] + num)
ans = max(ans, math.ceil(prefix_sum[-1] / len(prefix_sum)))
return ans