my solution
meta
- Clarify about what kind of solution we’re looking for.
- I’m going to assume that we want more of a low-level design for how to implement a single vending machine.
overview
A vending machine is a machine that stores various items and allows customers to select them and buy them.
requirements
- Should be able to store inventory for each unique item, keyed by the code that the user needs to enter to select it.
- Should be able to handle an order.
- Be ready for an input.
- After valid input, begin to start accepting money.
- After invalid input, go back to beginning state.
- After accepting enough money, dispense item.
- Handle case when no/not enough money comes for a certain period. Timeout?
- Provide an interface for restocking, where an employee can add items and update inventories.
non-functional requirements
- Consistent/durable.
- A user who inputs a valid amount of money should always get an item out of the machine, unless they walk away without finishing the transaction.
internal design
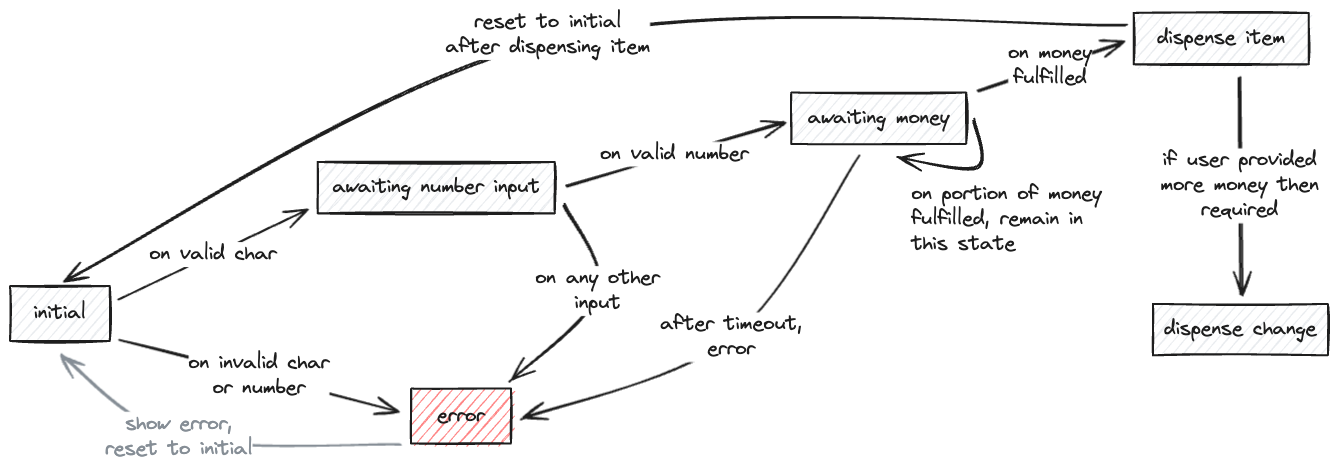
pseudocode
# keypad value or money entered, in cents
type Input = str | int
class State(abc):
@abstractmethod
def compute_next_state(input: Input) -> State:
pass
class InitialState(State):
def compute_next_state(input: Input) -> State:
if isinstance(input, str):
# could be even stricter, probably only
# a few letters are valid
if input.isalpha():
return NumberInputState()
return ErrorState()
class AwaitingMoneyState(State):
def __init__(self, cost):
self.cost_remaining = cost
def compute_next_state(input: Input) -> State:
# for simplicity, assume this checks that
# we are getting a money state
if instanceof(input, int) and input > 99:
self.cost_remaining -= input
if self.cost_remaining <= 0:
return DispenseItem(itemCode, self.cost_remaining)
# stay in this state
return self
class VendingMachine:
def __init__(self):
self.inventory = {
# key: [current_stock, price]
"A1": [12, 250],
"A2": [7, 200],
...
}
self.state = InitialState()
def dispense(self, itemCode):
self.inventory[itemCode][0] -= 1
def main():
# always listen for user input
while True:
# for simplicity, assume money being added and button presses
# can trigger this user_input() function
input = user_input()
next_state = self.state.compute_next_state(input)
if instanceof(next_state, ErrorState):
self.state = InitialState()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()