Given the root of a binary tree, return the same tree where every subtree (of the given tree) not containing a 1 has been removed.
A subtree of a node node is node plus every node that is a descendant of node.
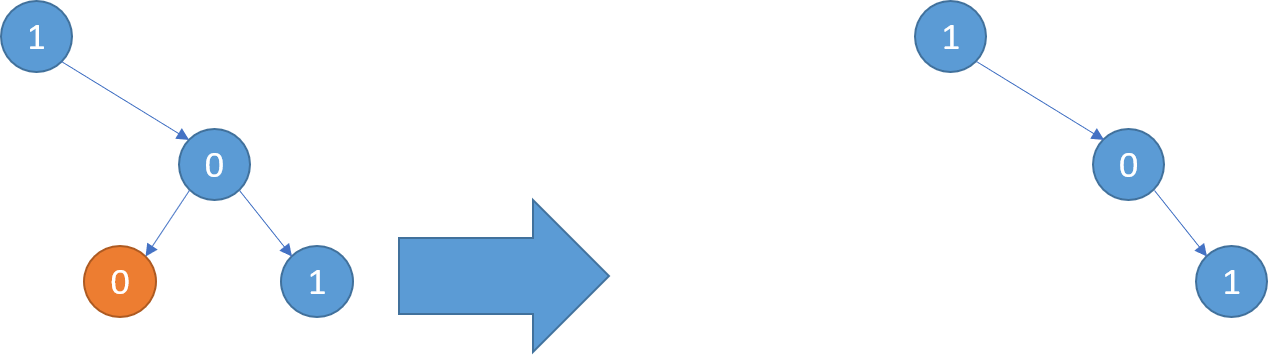
solution
We do a postorder traversal, where we first recursively prune the two children. Then, for the current node, if both children are None, then we know that both subtrees were either empty to begin with or pruned, meaning that the children of node did not contain any 1s.
Thus, the decision to prune the current node is now based on whether node.val == 1.
On the other hand, if either of the children are not None, that means they weren’t pruned and thus the tree rooted at node must contain a 1.
def pruneTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
def prune(node):
if not node:
return None
node.left = prune(node.left)
node.right = prune(node.right)
if not node.left and not node.right and node.val == 0:
return None
return node
return prune(root)